Amos Schonrock, MAN, RN, ST, PHN, CSSM, CNAMB, CNOR, NE-BC
Perioperative Practice and Safety Specialist
As perioperative professionals, the operating room team has a constant dedication and calling to the creation and maintenance of an environment that keeps our patient free from harm. As a vigilant guardian, the perioperative nurse is often at the forefront of this action. For positioning the perioperative patient, the nurse must use their senses to assess the patient’s well-being and current integumentary status as part of the pressure injury prevention assessment during all phases of care.
A device that can assist with the prevention of pressure and be used in conjunction with current operating tables is the gel overlay pad.
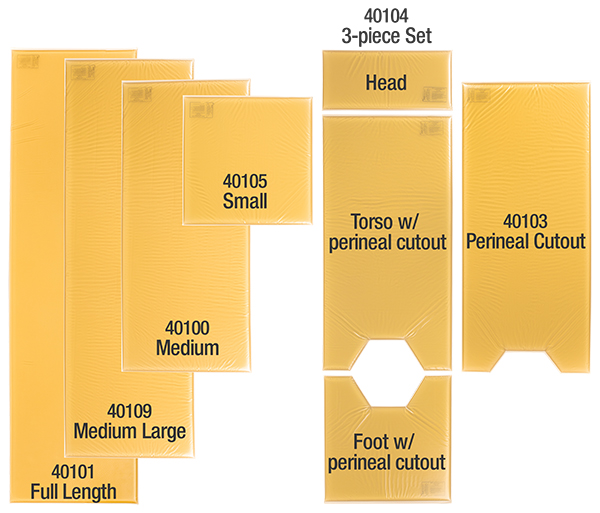
Action® O.R. Overlays
Available in various lengths, sizes, and shape configurations, the gel overlay features the same redistributive Akton® polymer as the Action® line of positioning devices and may be used with other items. The gel overlay may be used to meet an ideal standard for safe patient positioning and pressure injury prevention.
Safe patient positioning includes repositioning the patient’s head to decrease scalp pressure and subsequent breakdown and placing the patient’s body in physiologic alignment and away from metal portions of the bed, as well as padding hard surfaces that parts of the body may rest upon to prevent injury (Spruce, 2021). A gel overlay may be used to provide an ideal surface for the entire length of the patient’s anatomy and the full-length overlay aligns with the full length and width of the operating room table. When a patient’s anatomy or the necessary operative position requires part of the patient’s body not be elevated or free-floating, a secondary level of protection can be the gel overlay.
Gel overlays can help extend the life of older operating room table padding
The use of a gel overlay may extend or bring new life to using older operating room table pads. A gel overlay can be placed on top of an operating room surface that may be older and not have redistributive properties. This can provide the protection needed for patient pressure injury prevention and prolong the life and use of an older piece of operating room table padding.
The use of a gel overlay may also assist with maintaining patient normothermia in comparison to some older operating room table padding; the AKTON polymer is normothermic and when used in conjunction with a forced-air warming device may allow for increased compliance with the prevention of patient hypothermia.
Gel overlays can help prevent pressure injuries from head-to-toe
The addition of the gel overlay to the perioperative positioning toolbox is an ideal choice, as the use of the overlay doesn’t negate other Action® positioning devices. For example when in the lithotomy position the gel overlay may be used under the patient’s body in addition to the use of padded legholders; or when in the lateral position the gel overlays may be used along with an axillary roll to provide a pressure redistributive service from head to toe for those areas such as lateral femur, greater trochanter, and lateral malleolus that come in contact with the prominent areas of the operating room table.
As the perioperative nurse considers items that can provide pressuring injury prevention and are part of adjuncts to existing positioning devices, the gel overlay must remain at the top of the list for go to items.
Resources
References: Spruce, L. (2021). Positioning the patient. AORN Journal, 114(1), 75–84.
https://doi.org/10.1002/aorn.13442
B9019-000